CFD
Where 15 pipe diameters of straight pipe isn't available, we offer CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) optimisation services to ensure the most reliable and accurate measurements possible.
Why the need for CFD?
Simulating the Flow of Fluids
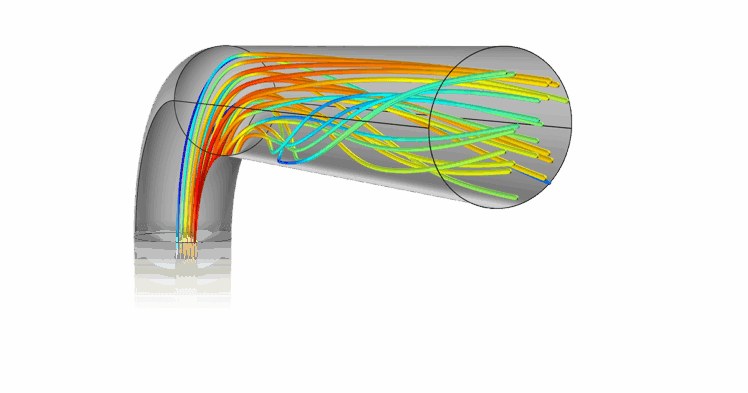
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) is a powerful tool that enables engineers to simulate the behavior of fluids or gases as they flow through various systems, particularly in complex scenarios where traditional flow measurement techniques may fall short. When it comes to measuring flare gas in systems where the ideal conditions, such as 15 diameters of straight piping, are not available, the flow profile can be distorted. This distortion can lead to inaccuracies in measurements, which can compromise the system’s efficiency and reliability.
In these cases, Fluenta employs CFD modeling to overcome the challenges posed by non-ideal piping arrangements. CFD allows for the detailed simulation of fluid dynamics within a system, enabling engineers to visualize how gases or liquids move, interact with surfaces, and respond to various obstacles within the piping. The process begins with creating a digital model of the piping system, which includes all relevant components such as bends, valves, and other flow obstructions. This model is then subjected to mathematical equations governing fluid flow, which are solved using high-powered computers.
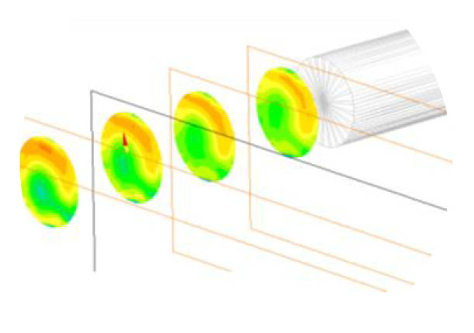
The CFD simulation produces a detailed map of the flow profile, showing how the fluid velocity, pressure, and turbulence vary throughout the system. This data is crucial for understanding how the flow behaves in non-ideal conditions, where the absence of fully developed flow profiles can lead to significant measurement errors. With this information, engineers can adjust the placement and calibration of flow meters to account for these variations, ensuring that the measurements are as accurate as possible.
Moreover, CFD modeling helps identify potential problem areas within the system, such as regions where flow might be excessively turbulent or where dead zones might occur, leading to poor mixing or flow separation. By addressing these issues through design adjustments or meter calibration, Fluenta ensures that the flow measurement system performs optimally, even under less-than-ideal conditions.
CFD Services
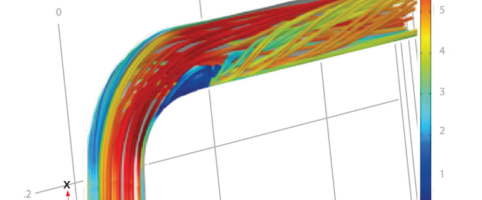
Mechanical Optimisation
In our mechanical optimisation package CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) is used to calculate optimal transducer angles
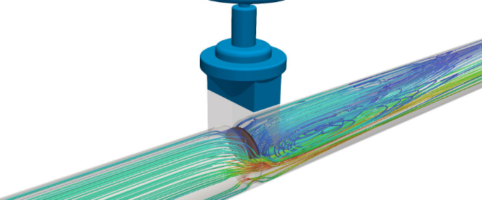
Advanced CFD Optimisation
In our advanced optimisation package, CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) is used to calculate the optimal transducer angles